Lessons learned by doing Branch-Per-Feature with Team Foundation Server.
Branch-Per-Feature with Team Foundation Server (TFS) Series Links
- How we got here…
- Kanban Stages
- Lessons Learned
In this post I’ll outline several of the issues/hiccups/features we found while attempting to apply Branch-Per-Feature with TFS.
260 Characters limit.
One of the first obstacles we ran into when attempting the Branch-Per-Feature with our TFS was the 260 Characters limit (you can read more here http://troyfarrell.com/blog/post/Maximum-file-path-length---Windows-and-TFS.aspx).
The largest offenders of this were artifacts added to a project as a result of doing an “Add Service Reference”. This feature created file names with the entire namespace in the file path. The way we got around this was the T4 replacement for "Add Service Reference" which helped keep some of the longer file paths shorter in our Silverlight projects. However it still rears it’s ugly head when we create a new branch and give a descriptive name that’s too long.
Which bring me to the next hiccup we run into.
Don’t RENAME a newly created branch. Delete it and re-create it with new name.
After a branch was created, if we decide the name for the branch wasn not good enough (either causes file path length issues, or it’s description isn’t clear enough), DON’T RENAME THE NEW BRANCH. Instead, choose to delete and re-create it. Clearly this has to be caught before commits are made to the new branch.
Why is this an issue?
In TFS, when you follow the simple steps to merge a feature from a branch into the trunk, you get to a point where all the changes made in the branch are checked out and staged to be merged into the trunk in your development environment. However when (or if) you’ve applied a rename to the branch at some stage in the lifetime of the branch, you don’t get a nice pretty list of files that changed and ready to be checked in, instead you get every file in the branch as though it were changed at some point in time. Sadly, this is usually not the case, and why I said earlier to catch the problem as soon as possible.
One of the great benefits of the branch/merge strategy is the final merge into the trunk is typically all changes required for a particular feature. When you have to go back to grapple some source control history debugging, it’s much easier to detect large changes from branch merges than sifting through tens of check-ins per file.
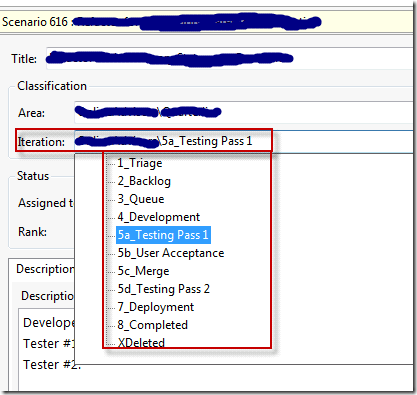
After the feature is complete and you start the steps required to merge the feature into the trunk, typically you only see the files that have changed get checked out and ready to be merged into the trunk. However, when a rename occurs on the branch it somehow tags every item as though it were changed. So the Merge back into the trunk ends up looking like the entire project changed. This makes the source diffing extremely difficult as I described in the Tester Pass 1 step in our kanban steps.
Can’t easily merge between different branches or grand-child branches (or at all, didn’t push hard enough to make it)
Another issue we’ve come across (which hasn’t road blocked us too bad) was the in-ability to merge between two different branches that stemmed from the same trunk or merging a grandchild branch into the grandparent (bypassing the child/parent).
A specific scenario we ran into was when Feature A was under development on a branch, and a developer was ready to start working on Feature B. Feature B had a dependency on some of the changes that had taken place in Feature A, however we wanted to deploy Feature A before Feature B was complete. As an experiment we thought we would just create Feature B’s branch straight from Feature A’s branch, however what this would have left us with when Feature A was merged into the Trunk was Feature B two levels away from the Trunk.
Although TFS allows this scenario, any changes to the trunk had to be pushed into Feature A’s branch before it could be pushed into Feature B’s branch, and come final merge time for Feature B, we couldn’t merge straight into the trunk. We would have had to first merge into Feature A’s branch and then do the final merge into the trunk. In the end we just held back the deployment of Feature A and both Feature A & B were developed in Feature A’s branch.
I read somewhere that this “could” be possible through some command line tools, however it wasn’t important enough to go through the pain and this would be much better if we could just use the existing TFS interface to accomplish this simple scenario.
I’m sure there are other tips/tricks I could outline here, but either they’re not coming to mind or they’re too basic to really care about. If I think of any, I’ll update this post further.

![ms727247.UI_Spy_Main_Window(en-us,VS.90)[1] ms727247.UI_Spy_Main_Window(en-us,VS.90)[1]](https://lh6.ggpht.com/_L6Vw0x_R3iw/SrBt19BG-II/AAAAAAAAAKs/yqtWK4N0wW4/ms727247.UI_Spy_Main_WindowenusVS.90%5B1%5D.png?imgmax=800)
.gif) Note: UI Spy is installed with the Microsoft Windows SDK. It is located in the \bin folder of the SDK installation path (uispy.exe) or can be accessed from the Start menu (Start\All Programs\Microsoft Windows SDK\Tools\UISpy).
Note: UI Spy is installed with the Microsoft Windows SDK. It is located in the \bin folder of the SDK installation path (uispy.exe) or can be accessed from the Start menu (Start\All Programs\Microsoft Windows SDK\Tools\UISpy).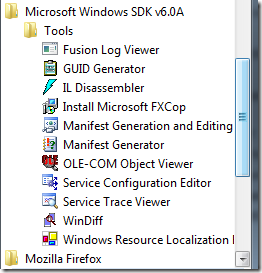



Thanks